|
| Magnetic level indicator with supplemental guided wave radar instrument Gemini Model - Magnetrol |
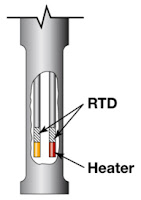
Essentially, a magnetic level gauge or magnetic level indicator, is a sight glass with enhancements that provide better readability and a form factor that enables the inclusion of additional level monitoring functions on the same device. Where a sight glass requires operator proximity to read liquid level, the magnetic level gauge's indicating scale, or flags, can be clearly viewed from a considerable distance. A sight glass gauge can also be hindered by difficulties in visually determining liquid level because of deterioration of the glass surface or properties of the liquid. Magnetic level gauges remove the need to observe the liquid directly by incorporating a float device within a tube connected to the liquid containing vessel. As the float moves in response to liquid level changes, its magnet causes the indicator flags on the scale to rotate and display either a black face to indicate no liquid present, or a colored face.
Magnetic level indicators are available with numerous options, including armored casings to protect the tube and float arrangement and limit switches to signal the attainment of specific level conditions. Combining a MLI with another level measurement technology, such as guided wave radar or magnetostrictive, can provide an analog process signal representing liquid level and serve as a redundant measuring device for critical applications.
The document included below provides illustrated detail about the devices and their proper application. Share your process measurement requirements and challenges with instrumentation experts. The combination of your process knowledge and their product application expertise will produce effective solutions.